Medics pen writer’s is a blog dedicated mainly for your daily medical tips, medical research articles, first aid tips and home made remedies for domestic illness and interesting medical articles.Medics is a blog where you learn more about Medical science, medical diagnosis, medical treatments, sex Education, scientific/Anatomical structures, surgery and treatments videos and lots more.
Get your daily healthy recipes

Your body goes quite a few hours without hydration as you sleep. Drinking a full glass of water in the morning can aid digestion, flush out toxins, enhance skin health and give you an energy boost.
HOME REMEDIES FOR MALERIA
Malaria is one of the deadly mosquito-borne diseases. Incidence of malaria cases and deaths caused by malaria are high in India.
Maleria is caused by a female anopheles mosquito
1.Sweet lime juice
Fresh juice extracted from sweet lime can be an effective home remedy for malaria. The juice is easy to digest and also have Vitamin C.
2.Tumeric
Turmeric is the super spice with amazing anti-oxidant and antimicrobial properties. Turmeric helps in flushing out harmful toxins from the body which build up because of plasmodium infection. Turmeric also helps in killing malaria parasite. Anti-inflammatory properties help in reducing muscle and joint pain, which are common in malaria. Drink a glass of turmeric milk every night to deal with malaria.
3.Grapefruit
Raw grapefruit can help in reducing intensity of malarial infection. To make grapefruit juice, you can boil grapefruit in hot water and strain the pulp. Grapefruit juice has a quinine-like substance which helps in reducing symptoms of malaria. However, do take your doctor’s advice before taking grapefruit juice.
This season can trigger asthma and allergies. Asthmatic patients should always keep the inhaler handy and avoid dust as much as possible. This dry cold dusty season triggers sickle cell disease (SCD) as well. Patients should drink plenty of water and avoid outdoor activities as much as possible.
HERE ARE THE FOLLOWING TIPS TO STAY HEALTHY DURING THIS HARMATTAN SEASON
1) Drink plenty of water to prevent dehydration
2) wash your eyes regularly to avoid red eyes which is common in during harmattan
3) Cover your nose and mouth with a mask or towel when it is dusty
4) Avoid or reduce outdoor activities, especially if you have allergies
5) Stay indoors to avoid dust inhalation of harmful particles comling with the wind
6) Wear clothes that keep your body warm
others are
Come to the clinic if you have red, itchy, and watery eyes.
Get medical help if you have running, itchy, sneezing, and stuffy nose
Keep the doors and windows closed
Always use moisturizers to prevent dry skin and dry palms
Use lip balm to prevent cracked lips
medics_writers
#stay safe
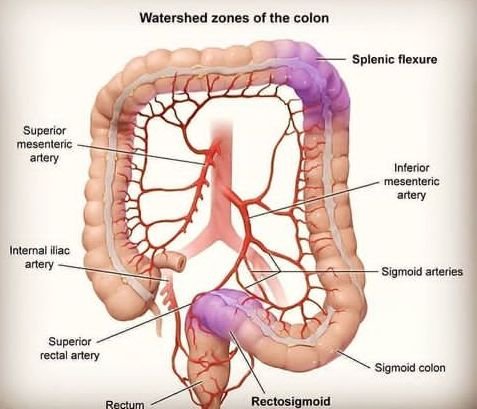
COLON
The colon is one of the most important organ that helps in digestion, the colon is like a stomach pipe that helps in transportation and absorption of food nutrients including food particles. Colon also helps in the secretion of some materials that helps in digestion.
The colon is also known as the large bowel or large intestine. It is an organ that is part of the digestive system (also called the digestive tract) in the human body. The digestive system is the group of organs that allow us to eat and to use the food we eat to fuel our bodies.
Food begins in the mouth where it is chewed by the teeth into smaller pieces. Once swallowed the food travels into the esophagus which connects to the stomach.
In the stomach food is further broken down to liquid and passed on to the small bowel (intestine).
In the small bowel, the food breakdown continues with the assistance of the pancreas, liver and gallbladder. Here is where all the important vitamins and nutrients in food are absorbed.
What is left over, which is mostly liquid, then moves into the colon. The water is absorbed in the colon. Bacteria in the colon break down the remaining material. Then the colon moves the leftover material into the rectum.
The rectum is like a storage-holder for this waste. Muscles in the rectum move the waste, called stool, out of the body through the anus.
medics_ writer’s
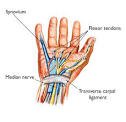
THE CARPAL TUNNEL The carpal tunnel is a narrow passageway found on the anterior portion of the wrist. It serves as the entrance to the palm for several tendons and the median nerve.
It’s a shallow depression found in the anterior portion of wrist and it’s also indicates an area of transition between the forearm and the palm.
In this short post we shall discuss detailed points about the carpal tunnel and the carpal tunnel Syndrome.
ANATOMICAL CONTENTS OF THE CARPAL TUNNEL
The carpal tunnel contains a total of 9 tendons, surrounded by synovial sheaths, and the median nerve. The palmar cutaneous branch of the median nerve is given off prior to the carpal tunnel, travelling superficially to the flexor retinaculum.
Tendons
The tendon of flexor pollicis longus
Four tendons of flexor digitorum profundus
Four tendons of flexor digitorum superficialis
The 8 tendons of the flexor digitorum profundus and flexor digitorum superficialis are surrounded by a single synovial sheath. The tendon of flexor pollicis longus is surrounded by its own synovial sheath. These sheaths allow free movement of the tendons.
Sometimes you may hear that the carpal tunnel contains another tendon, the flexor carpi radialis tendon, but this is located within the flexor retinaculum and not within the carpal tunnel itself!.
CARPAL TUNNEL SYNDROME
The carpal tunnel Syndrome is one of the common trauma affecting the carpal tunnel and is due to a very severe trauma affecting the median nerve in the carpal tunnel.
Compression of the median nerve within the carpal tunnel can cause carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS). It is the most common mononeuropathy and can be caused by thickened ligaments and tendon sheaths. Its aetiology is, however, most often idiopathic. If left untreated, CTS can cause weakness and atrophy of the thenar muscles.
Clinical features include numbness, tingling and pain in the distribution of the median nerve. The pain will usually radiate to the forearm. Symptoms are often associated with waking the patient from their sleep and being worse in the mornings.
Tests for CTS can be performed during physical examination:
Tapping the nerve in the carpal tunnel to elicit pain in median nerve distribution (Tinel’s Sign)
Holding the wrist in flexion for 60 seconds to elicit numbness/pain in median nerve distribution (Phalen’s manoeuvre)
Treatment involves the use of a splint, holding the wrist in dorsiflexion overnight to relieve symptoms. If this is unsuccessful, corticosteroid injections into the carpal tunnel can be used. In severe case, surgical decompression of the carpal tunnel may be required.
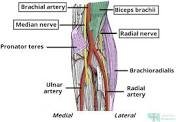
THE CUBITAL FOSSA
The cubital fossa is a triangular depression which marks the area of transition between the arm and the forearm. The cubital fossa is located above the elbow joint and located anteriorly in a balanced anatomical position.
The cubital fossa is an area of transition between the anatomical arm and the forearm. It is located as a depression on the anterior surface of the elbow joint.
BORDERS OF THE CUBITAL FOSSA
The cubital fossa is triangular in shape, and thus has three borders, mainly bounded by the muscles of the arm and forearm.
Lateral border – medial border of the brachioradialis muscle.
Medial border – lateral border of the pronator teres muscle.
Superior border – hypothetical line between the epicondyles of the humerus.
The floor of the cubital fossa is formed proximally by the brachialis, and distally by the supinator muscle. The roof consists of skin and fascia, and is reinforced by the bicipital aponeurosis. Within the roof runs the median cubital vein, which can be accessed for venepuncture.
CONTENTS OF THE CUBITAL FOSSA
The cubital fossa is mainly filled with fats.
prominent contents include;
The contents of the cubital fossa include vessels, nerves and the biceps tendon (lateral to medial):
Radial nerve – this is not always strictly considered part of the cubital fossa, but is in the vicinity, passing underneath the brachioradialis muscle. As it does so, the radial nerve divides into its deep and superficial branches.
Biceps tendon – runs through the cubital fossa, attaching to the radial tuberosity, just distal to the neck of the radius.
Brachial artery – supplies oxygenated blood to the forearm. It bifurcates into the radial and ulnar arteries at the apex of the cubital fossa.
Median nerve – leaves the cubital between the two heads of the pronator teres. It supplies the majority of the flexor muscles in the forearm.
CLINICAL CORRELATE
Venepuncture
The median cubital vein is located superficially within the roof of the cubital fossa. It connects the basilic and cephalic veins, and can be accessed easily – this makes it a common site for venepuncture.
